
S90
24th European Congress of Psychiatry / European Psychiatry 33S (2016) S72–S115
4
RWTH Aachen University, Department of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy
and Psychosomatics, Aachen, Germany
∗
Corresponding author.
Introduction
The aim of the FP7-European funded project TRIM-
AGE is to create a trimodal, cost-effective imaging tool consisting
of PET/MR/EEG to enable effective early diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Objective
In the scope of this project we are interested in
the multimodal assessment of response inhibition. The loudness
dependence of auditory evoked potential (LDAEP) is a suitable
biomarker of inhibitory action in signal processing. Variations in
response inhibition can have great impact on different aspects of
life. Individuals with reduced capability of inhibitory control have
a tendency to impulsive behavior. Studies showed that they have
stronger LDAEP values. Patients with schizophrenia may exhibit
alterations in the responsiveness to sensory stimuli. Thus, a reduced
LDAEP was found in these patients. However, these deviances dif-
fered in clinical features of the disorder. Therefore, we would like to
further elucidate the relationship betweenmultimodal neuroimag-
ing methods and dimensions of symptoms, observable behavior,
personality traits and general psychopathological dysfunction.
Methods
A sample of 20 healthy controls and 20 patients with
manifest schizophrenia will be examinedwith the LDAEP paradigm
in a trimodal approachwith customary imaging tools. PETmeasure-
ments with the radiotracer [11C]-flumazenil will be used to assess
the binding potentials of GABA-A receptors. MRS will provide data
about GABA concentrations. Simultaneously recorded EEG-fMRI
data will permit new insight in the relationship between LDAEP
and impulsivity.
Discussion
The project will use alternative approaches to psy-
chiatric classification. Response inhibition in sensory processing
will be investigated from different angles (biochemical, neuro-
physiological, and neuroanatomical) and combined with psycho-
logical characteristic values.
Disclosure of interest
The authors have not supplied their decla-
ration of competing interest.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.01.050FC47
A diffusion tensor imaging study of
white matter microstructure
concerning suicidal ideation in major
depressive disorder
H. Zhang
1 ,∗
, Z. Jia
21
West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Radiology, Chengdu, China
2
West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Nuclear medicine,
Chengdu, China
∗
Corresponding author.
Introduction
Suicide is a serious public health problem.
Microstructural abnormalities of white matter (WM) in major
depressive disorder (MDD) patients had been studied with diffu-
sion tensor image (DTI) before. However, little is known regarding
suicidal ideation (SI).
Objectives
To use diffusion tensor imaging to characterize abnor-
malities of white matter integrity in major depressive disorder
patients with and without SI.
Methods
Sixteen depressive patients with SI, 16 depressive
patients without SI and 32 age- and gender-matched healthy con-
trols received MRI scans on a 3T magnet. Whole brain voxel-based
analysis was used to compare fractional anisotropy (FA) across the
three groupswith threshold at
P
< 0.005 (uncorrected) at voxel level
and 50 for cluster size with SPM8. Pearson analyze was conducted
to examine the association between clinical measurements and
regional FA value.
Results
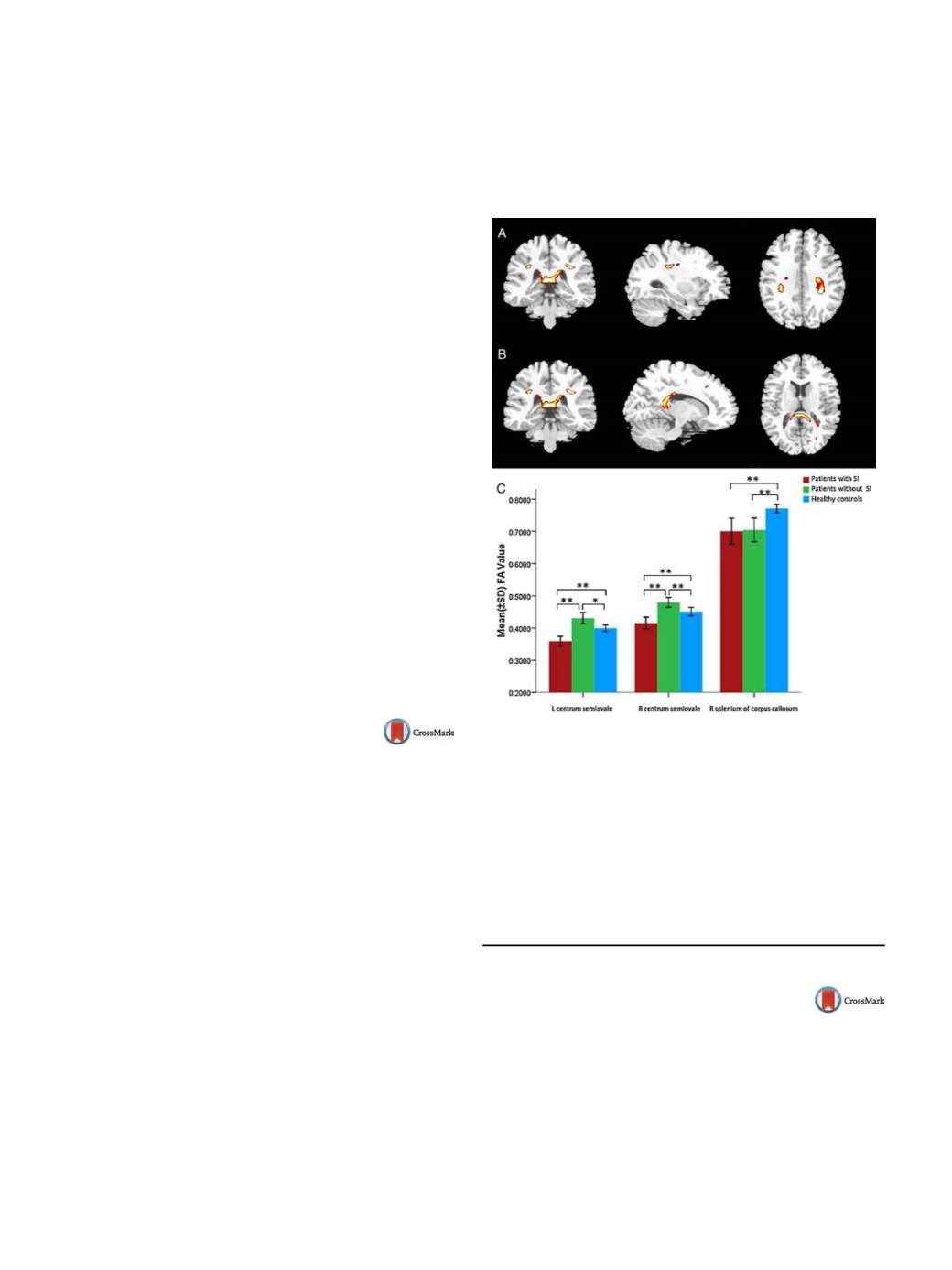
The three groups had significant differences of FA in the
left centrum semiovale (peak Z = 4.64 at
−
30,
−
38, 34), right cen-
trum semiovale (peak Z = 3.54 at 32,
−
34, 32) and right splenium of
corpus callosum (peak Z = 4.64 at 4,
−
34, 12;
Fig. 1 ).We also found a
negative correlation between mean regional FA values in the white
matter under the left centrum semiovale and the intensity of sui-
cidal ideation scores (
r
=
−
0.563,
P
= 0.023).
Conclusion
Suicidal ideation is associated with microstructure
abnormalities of thewhitematter in centrumsemiovale and corpus
callosum.
Fig. 1
Brain regions differed significantly among groups. A. Bilat-
eral centrum semiovale. B. Right splenium of corpus callosum.
C. Patients tested.
Disclosure of interest
The authors have not supplied their decla-
ration of competing interest.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.01.051Obsessive-compulsive disorder
FC48
Actions speak louder than words:
Enhanced action tendencies in
obsessive-compulsive disorder:
An ERP study
A. Dayan Riva
1 ,∗
, A. Berger
2, G. Anholt
21
Beer Sheva, Israel
2
Ben Gurion University of the Negev, Psychology, Beer Sheva, Israel
∗
Corresponding author.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is characterized by repeated
thoughts and behaviors. Several studies have detected defi-
cient response inhibition ability in individuals with OCD, leading
researchers to suggest this deficit as an endophenotype of OCD.


















