
S96
24th European Congress of Psychiatry / European Psychiatry 33S (2016) S72–S115
Results
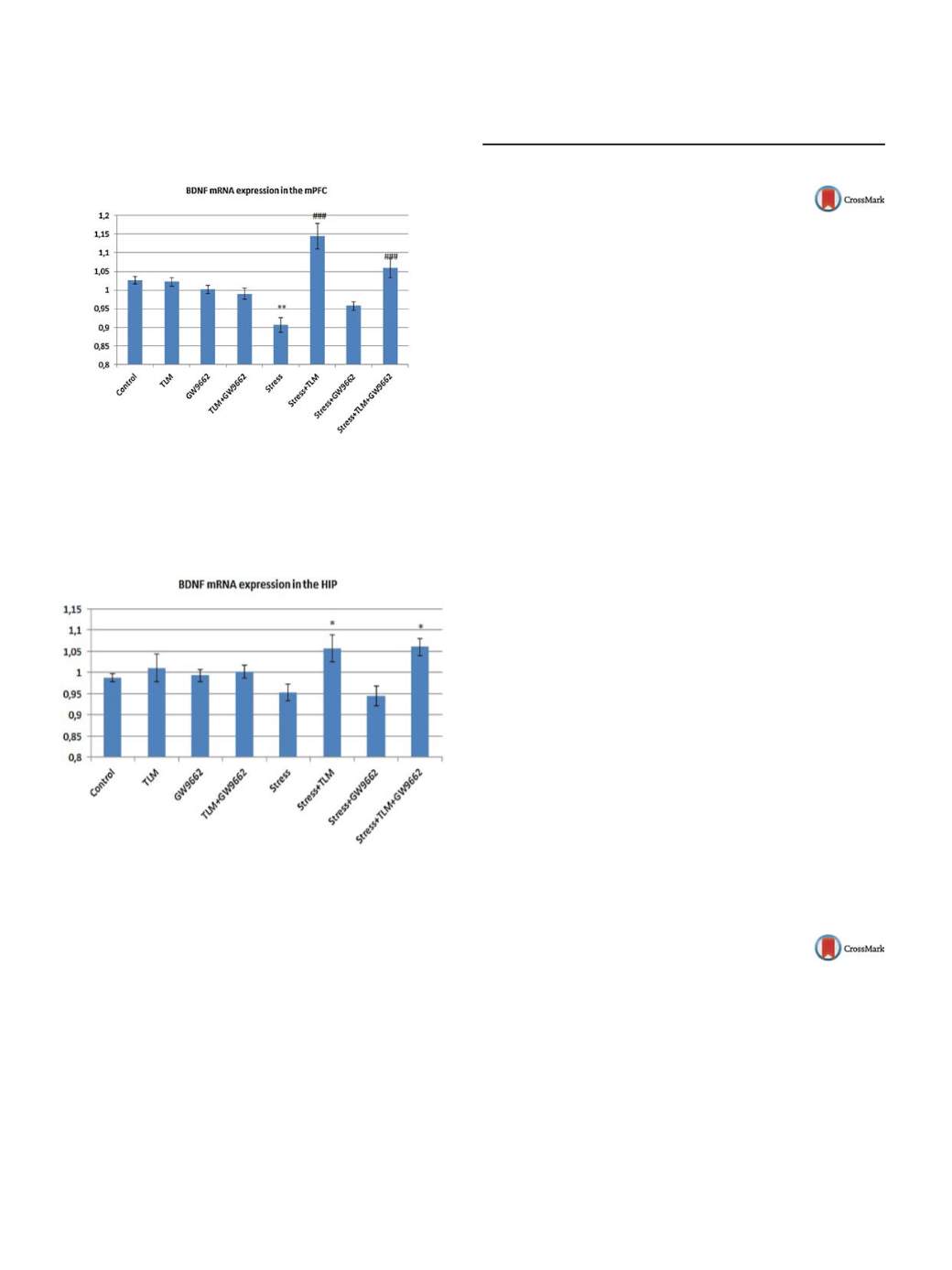
Alterations of mRNA expression of BDNF are shown on
Figs. 1 and 2 .Conclusions
AT1 receptor blockade restores cognitive functions
in chronically stressed subjects, which is associated with changes
in primarily cortical gene expression.
Fig. 1
Effect of chronic stress (2.5 h, 21 days), chronic TLM
(1mg/kg, 21 days), chronic GW9662 (0.5mg/kg. 21 days) or
all in combination on mRNA BDNF expression in the mPFC
(BDNF/Tbp ratio). Bars represent mean
±
SEM;
n
= 5; **
P
< 0.01;
Control vs. Stress; ###
P
< 0.001 Stress vs. Stress + TLM and Stress
vs. Stress + TLM+ GW9662.
Fig. 2
Effect of chronic stress (2.5 h, 21 days), chronic TLM
(1mg/kg, 21 days), chronic GW9662 (0.5mg/kg, 21 days) or all
in combination on mRNA BDNF expression in the HIP (EDNF/Tbp
ratio). Bars represent means
±
SEM;
n
= 5; *
P
< 0.05; Stress vs.
Stress + TLM and Stress vs. Stress + TLIVH-GW9662.
Disclosure of interest
The authors have not supplied their decla-
ration of competing interest.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.01.062Psychosurgery and stimulation methods
(ECT, TMS, VNS, DBS)
FC59
Neuropsychiatric consequences of
deep brain stimulation surgeries in
the patients affected by chronic
movement disorders: A brief report
S. Mahdavi
1 ,∗
, S.K. Malakouti
2, B. Naji
2, M. Asadi
1, S. Kahani
31
Iran University of Medical Sciences, psychiatry, Tehran, Iran
2
School of Behavioral Sciences and Mental Health, Iran University of
Medical Sciences, psychiatry, Tehran, Iran
3
Rasoul Akram Hospital, Iran University of Medical Sciences,
psychiatry, Tehran, Iran
∗
Corresponding author.
The main surgical procedure for PD and other chronic movement
disorders is deep brain stimulation. DBS has been reported to
have specific consequences such as decline in verbal fluency and
episodes of depression.
We designed an interventional study in 12 patients affected by
Parkinson, dystonia and tic who underwent DBS surgery. Patient
assessed before surgery, one month and one year after surgery.
The results proved a significant improvement in SF36. The
Hamilton’s anxiety scale showed an overall but insignificant
improvement. The mean of scores of the BDI had a great drop one
month after surgery but a raise at the 12th month (insignificant
pattern).
Pearson’s correlation test showed a significant negative correlation
between age and the SF36 scores. The BDI’s scores were assessed in
relation with age. Although there was no actual relation between
them before surgery, we detected a positive correlation between
them after one year.
Conclusion
The pattern of changes can be related with the dif-
ferences between perioperative expectations and real long-term
outcomes. Correlations between changes seen in BDI and SF36
scores with age can be considered as a confirmatory evidence for
this idea.
All cases showed an insignificant gradual decline in digit span test,
which may be independent of the surgical procedure. Although the
COWA test could not prove a significant deterioration in verbal flu-
ency but a slight decline after one year was obvious, in addition to
one patient who turned aphasic during this period.
The outcomes showed that the benefits of DBS outweigh the slight
risk of developing depression.
Disclosure of interest
The authors have not supplied their decla-
ration of competing interest.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.01.063FC60
Transcranial direct current
stimulation in treatment – resistance
unipolar major depressive disorder
M. Asadi
∗
, S. Mahdavi
Tehran University of medical science, psychiatry, Tehran, Iran
∗
Corresponding author.
Objective
MDD is a common, chronic and recurrent illness .it is
essential to reach full remission in acute treatment. tDCS is a non-
invasive brain stimulation that uses direct electrical currents to
stimulate specific parts of the brain.
Aim
Is to assess the effectiveness of tDCS in patients with treat-
ment resistance MDD.
Method
Eighty outpatients of a psychiatric clinic were selected.
Subjects meet (DSM-IV) diagnostic criteria for MDD. All patients
had failed to respond to at least two standard antidepressant


















