
24th European Congress of Psychiatry / European Psychiatry 33S (2016) S349–S805
S371
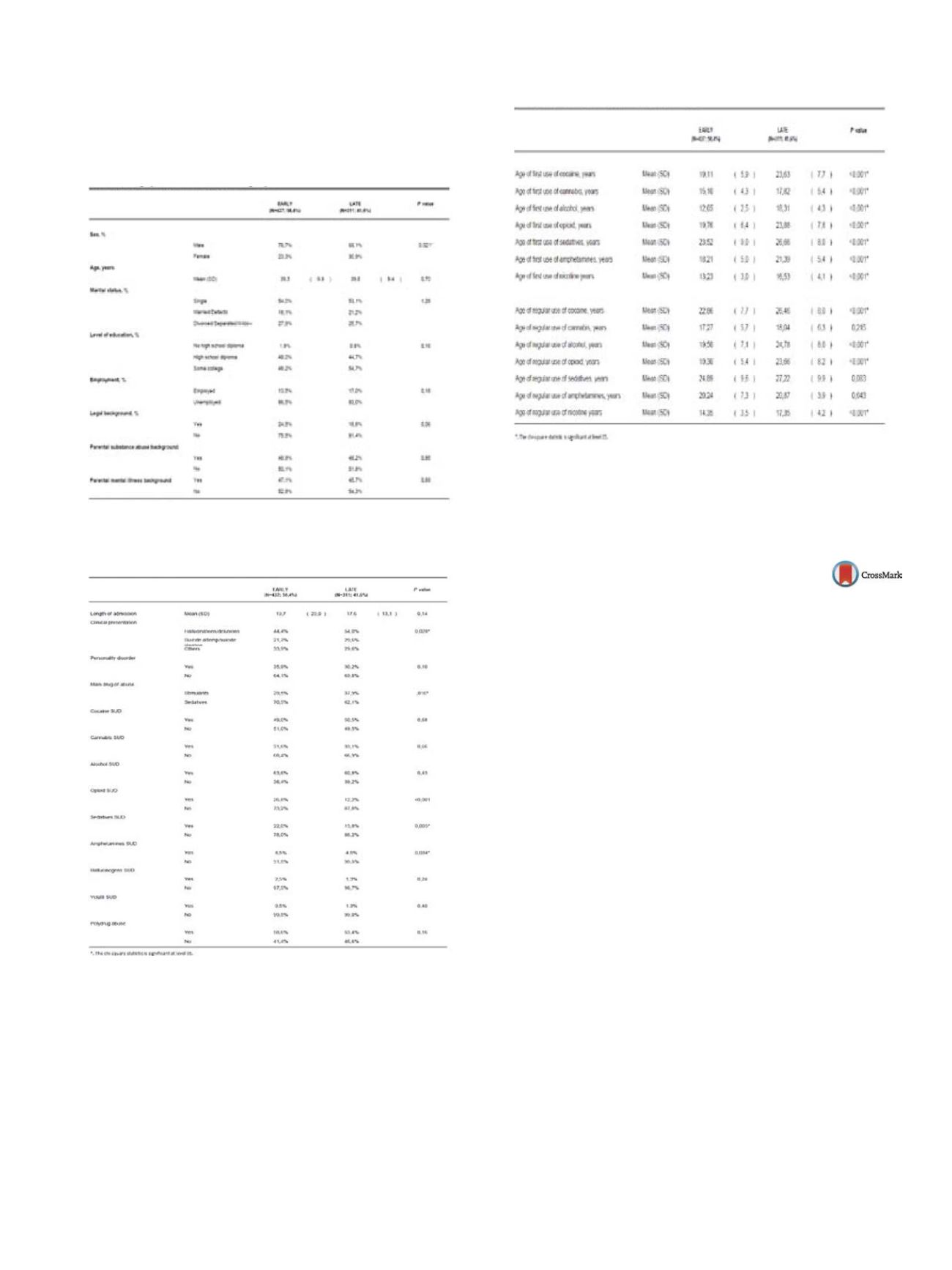
amphetamine use. They also had earlier consumptions of other sub-
stances and earlier problematic consumptions of cocaine, alcohol,
opioids and nicotine, what probably means greater severity of drug
addiction in the long run.
Table 1
Demographic characteristics of both groups.
Table 2
Clinical and functional variable at admission in both
groups.
Table 3
Historical data about age of drug use in both groups.
Disclosure of interest
The authors have not supplied their decla-
ration of competing interest.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.01.1051EV67
Assessment of comparing psychiatric
disorders in mono-opioid and
poly-opioid dependents, according to
SCL90-R Test, in cessation drug
centers in Kerman City, Iran, 2015
A. Ghaffarinejad , A. Mehdizadeh Zare Anari
∗
, N. Mahdinia
Kerman university of medical sciences, psychiatry, Kerman, Iran
∗
Corresponding author.
Background
One of the hygienic-psychic issues throughout the
country is drug dependency, which causes numerous problems in
the society. These individuals are vulnerable in front of psychiatric
disorders, and this is seen more in poly-opioid dependents.
Methods
This causal-comparative research is cross-sectional
study. Among of the poly-opioid and mono-opioid dependents in
cessation drug centers inKerman 1392–93, a sample of 234 persons
(117 poly-opioid dependents and 117 mono-opioid dependents)
were chosen randomly to answer SCL90-R test and demographic
questionnaire. Analysis performed by SPSS18 by use of average,
standard deviation, frequency and
t
test.
Findings
According to the findings, on the whole somatization,
anxiety, depression, phobia, sensitivity, psychosis, paranoid idea,
aggression and obsessive-compulsive were significantly different
(
P
< 0.05) between mono-opioid and poly-opioid dependents, so
that these 9 psychotic disorders in poly-opioid dependents were
more than mono-opioid dependents.
Conclusion
Finding of this research showed that these psychiatric
disorders in several drugs abusers are more than one drug abusers.
Keywords
Psychiatric disorders; Poly-opioid dependents;
Mono-opioid dependents
Disclosure of interest
The authors have not supplied their decla-
ration of competing interest.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.01.1052

















